Template:Tires: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Dingzhou Cao (talk | contribs) m (→Tire Example) |
Dingzhou Cao (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
*If the tire fails due to wear the tire is replaced with a new one (wear is repaired ''as-good-as-new''). | *If the tire fails due to wear the tire is replaced with a new one (wear is repaired ''as-good-as-new''). | ||
*If the tire fails due to a puncture, it is patched up and placed biack into service (repaired ''as-bad-as-old''). | *If the tire fails due to a puncture, it is patched up and placed biack into service (repaired ''as-bad-as-old''). | ||
*When a primary tire (RF, LF, RR or LR) fails it is replaced with the spare (SP) until that tire is restored. Once restored the tire is put back in | *When a primary tire (RF, LF, RR or LR) fails it is replaced with the spare (SP) until that tire is restored. Once restored the tire is put back in its original position and the spare is removed and put back for later use. | ||
[[Image:TireEx.png|thumb|center|500px]] | [[Image:TireEx.png|thumb|center|500px]] | ||
Revision as of 21:34, 5 October 2011
Tire Example
Consider a car with four regular tires (RF, LF, RR, LR) and a spare tire (SP). Furthermore assume that each tire can fail based on two failure modes, wear and puncture, and:
- The wear failure modes follows a Weibull distribution with Beta = 1.5, Eta = 600 hours.
- The puncture failure mode folllows an exponential distribution with a mean of 2 months.
- Regardless of the failure mode, the repair duration (of both wear and puncture) follows a Weibull distribution with Beta = 1.5,Eta = 100 hours.
- If the tire fails due to wear the tire is replaced with a new one (wear is repaired as-good-as-new).
- If the tire fails due to a puncture, it is patched up and placed biack into service (repaired as-bad-as-old).
- When a primary tire (RF, LF, RR or LR) fails it is replaced with the spare (SP) until that tire is restored. Once restored the tire is put back in its original position and the spare is removed and put back for later use.
Purposes
The purpose of this example is to illustrate the following options in SCT:
- State Upon Repair: Always ON, Always OFF
- Activate a block if any item from these associated maintenance group(s) goes down.
- Deactivate a block if any item from these associated maintenance group(s) is restored.
- Deactivate a block if any item from these associated maintenance group(s) goes down.
- Activate a block if any item from these associated maintenance group(s) is restored.
BlockSim Solution
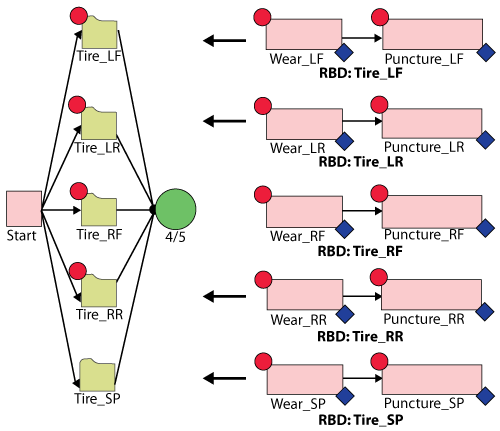
- To model this system, six diagrams are created: Car, Tire_LF, Tire_LR, Tire_RF, Tire_RR and Tire_SP with Car being the main diagram. Create the diagrams as follows:
- First create diagram Tire_LF with two blocks in series. Block Wear_LF represents Wear failure mode and Puncture_LF represents Puncture failure mode for Tire_LF respectively.
- Block Wear_LF belongs to maintenance group "Wear_LF" and Block Puncture_LF belongs to maintenance group "Puncture_LF".
- Block Wear_LF has State Change Triggers (SCT), its initial state is ON, and the state upon repair is "Always On". If any item from maintenance group "Puncture_LF" goes down, deactivate this block and if any item from maintenance group "Puncture_LF" is restored, activate this block.
- Block Puncture_LF also has State Change Triggers (SCT), its initial state is ON, and the state upon repair is "Always On". If any item from maintenance group "Wear_LF" goes down, deactivate this block and if any item from maintenance group "Wear_LF" is restored, activate this block.
- Create the other three diagrams (Tire_LR, Tire_RF and Tire_RR) following the same logic.
- In diagram Tire_SP, there are two blocks in series. Block Wear_SP represents Wear failure mode and Puncture_SP represents Puncture failure mode for spare tire respectively. Block Wear_SP belongs to maintenance group "Wear_SP" and Block Puncture_SP belongs to maintenance group "Puncture_SP".
- Block Wear_SP has State Change Triggers (SCT), its initial state is OFF, and the state upon repair is "Always OFF". If any item from maintenance group "Puncture_SP" goes down, deactivate this block and if any item from maintenance group "Puncture_SP" is restored, activate this block. If any item from maintenance group "Main Tires" goes down, activate this block and if any item from the maintenance group "Main Tires" is restored, deactivate this block.
- Block Puncture_SP has State Change Triggers (SCT), its initial state is OFF, and the state upon repair is "Always OFF". If any item from maintenance group "Wear_SP" goes down, deactivate this block and if any item from maintenance group "Wear_SP" is restored, activate this block. If any item from maintenance group "Main Tires" goes down, activate this block and if any item from the maintenance group "Main Tires" is restored, deactivate this block.
- In the diagram Car, there are five subdiagram blocks Tire_LF, Tire_LR, Tire_RF, Tire_RR and Tire_SP (each referencing/pointing to the five diagrams with the same names).
- In diagram Car, subdiagram blocks Tire_LF, Tire_LR, Tire_RF and Tire_RR belong to maintenance group "Main Tires".
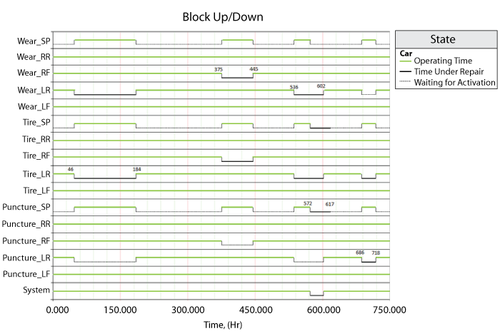
Blocks Up/Down plot
The system event log is shown in Figure below and is as follows (only blocks have failures are plot):
- At 46, Block Wear_LR fails and brings down subdiagram Tire_LR. At the same time, it turns Block Puncture_LR OFF. Subdiagram Tire_LR goes down and actives Block Wear_SP and Puncture_SP, and subdiagram Spare is turn ON too.
- At 184, Block Wear_LR is done with repair. According to setting, it is always ON upon repair (is restored). The restoration of Block Wear_LR activates Block Puncture_LR and thus subdiagram Tire_LR is ON. The restoration of subdiagram Tire_LR deactives Block Wear_SP and Puncture_SP, and subdiagram Tire_SP is turn OFF too.
- At 375, Block Wear_RF fails and brings down subdiagram Tire_RF. At the same time, it turns Block Puncture_RF OFF. Subdiagram Tire_RF goes down and actives Block Wear_SP and Puncture_SP, and subdiagram Tire_SP is turn ON too.
- At 445, Block Wear_RF is done with repair. According to setting, it is always ON upon repair (is restored). The restoration of Block Wear_RF activates Block Puncture_RF and thus subdiagram Tire_RF is ON. The restoration of subdiagram Tire_RF deactives Block Wear_SP and Puncture_SP, and subdiagram Tire_SP is turn OFF too.
- At 536, Block Wear_LR fails again and brings down subdigram Tire_LR. At the same time, it turns Block Punture_LR OFF. Subdiagram Tire_LR goes down and actives Block Wear_SP and Puncture_SP, and the subdiagram Tire_SP is turn ON too.
- At 572, Block Puncture_SP fails and brings down subdigram Tire_SP. At the same time, it turns Block Wear_SP OFF. Since subdigram Tire_LR is already down at this time. Thus the system is down.
- At 602, Block Wear_LR is done with repar. According to setting, it is always ON upon repair(is resotred). The restoration of Block Wear_LR activates Block Puncture_LR and thus subdigram Tire_LR is ON. The restoration of subdigram Tire_LR should deactive Block Wear_SP and Puncture_SP. However, Wear_SP is already OFF and Puncture_SP is already down at this time, thus nothing happens. The system is ON at this time due to the restoration of subdiagram Tire_LR.
- At 617, Block Puncture_SP is done with repair. According to setting, it is always OFF upon repair.
- At 686, Block Puncture_LR fails and brings down subdigram Tire_LR. At the same time, it turns Block Wear_LR OFF. Subdigram Tire_LR goes down and actives Block Wear_SP and Puncture_SP, and the subdigram Tire_SP is turn ON too.
- At 718, Block Puncture_LR is done with repair. According to setting, it is always ON upon repair(is restored). The restoration of Block Puncture_LR actives Block Wear_LR and thus subdiagram Tire_LR is ON. The restoration of subdigram Tire_LR deactives Block Wear_SP and Puncture_SP, and the subdigram Tire_SP is turn OFF too.