Box Behnken RSM: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Lisa Hacker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Lisa Hacker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Reference Example|{{Banner DOE Reference Examples}}}} | {{Reference Example|{{Banner DOE Reference Examples}}}} | ||
This example validates the calculation of the Box-Behnken RSM method in | This example validates the calculation of the Box-Behnken RSM method in Weibull++. | ||
{{Reference_Example_Heading1}} | {{Reference_Example_Heading1}} | ||
The data are from Example 7.5 on page 347 in the book ''Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 2nd Edition,'' by Raymond H. Myers and Douglas C. Montgomery, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2002. | |||
{{Reference_Example_Heading2}} | {{Reference_Example_Heading2}} | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
!Temperature (A) | !Temperature (A) | ||
!Agitation (B) | !Agitation (B) | ||
!Rate | !Rate (C) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| High (+1)||200||10||25 | | High (+1)||200||10||25 | ||
| Line 23: | Line 21: | ||
|} | |} | ||
The viscosity of the resin was recorded as an indirect measure of molecular weight. | |||
{| {{Table|23%}} | |||
{| {{Table| | |||
!Standard order | !Standard order | ||
!A | !A | ||
| Line 32: | Line 30: | ||
!Y | !Y | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1||-1||-1||0||53 | |style="width:100px;"|1||-1||-1||0||53 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2||+1||-1||0||58 | | 2||+1||-1||0||58 | ||
| Line 61: | Line 59: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 15||0||0||0||62 | | 15||0||0||0||62 | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{Reference_Example_Heading3}} | {{Reference_Example_Heading3}} | ||
| Line 70: | Line 67: | ||
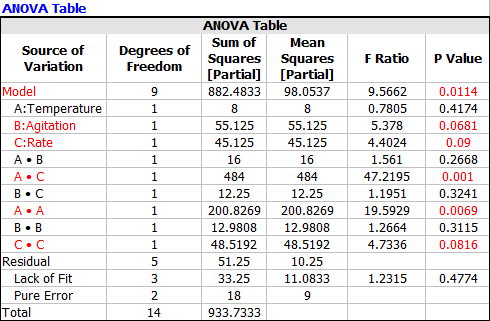
From the book, the ANOVA table (partial sum of squares) is: | From the book, the ANOVA table (partial sum of squares) is: | ||
{| {{Table}} | {| {{Table|50%}} | ||
!Source | !Source | ||
!Partial SS | !Partial SS | ||
| Line 76: | Line 73: | ||
!Mean Square | !Mean Square | ||
!F value | !F value | ||
!Prob>F | !Prob > F | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Model||882.48||9||98.05||9.57||0.0114 | | Model||882.48||9||98.05||9.57||0.0114 | ||
| Line 86: | Line 83: | ||
| C||45.13||1||45.13||4.40||0.09 | | C||45.13||1||45.13||4.40||0.09 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <math>A^2</math>||200.83||1||200.83||19.59||0.0069 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| B^2||12.98||1||12.98||1.27||0.3115 | | <math>B^2</math>||12.98||1||12.98||1.27||0.3115 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| C^2||48.52||1||48.52||4.73||0.0816 | | <math>C^2</math>||48.52||1||48.52||4.73||0.0816 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| AB||16.00||1||16.00||1.56||0.2668 | | AB||16.00||1||16.00||1.56||0.2668 | ||
| Line 104: | Line 101: | ||
| Pure error||18||2||9.00|||| | | Pure error||18||2||9.00|||| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Cor total||933.73||14||||| | | Cor total||933.73||14|||||| | ||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
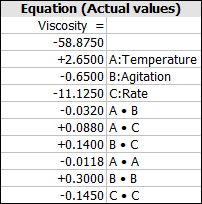
The final equation in terms of actual factors: | |||
::<math>\begin{align} | |||
Viscosity=-58.875+2.65 * Temp-0.65 * Agitation-11.125*Rate-0.0118*Temp^2+0.3*Agitation^2 \\ | |||
-0.145*Rate^2-0.032*Temp*Agitation+0.088*Temp*Rate+0.14*Agitation*Rate | |||
\end{align}</math> | |||
| Line 118: | Line 119: | ||
[[Image:behnken_anova.png|center]] | [[Image:behnken_anova.png|center]] | ||
The final equation in terms of actual factors is: | The final equation in terms of the actual factors is: | ||
[[Image:behnken_final.png|center]] | [[Image:behnken_final.png|center]] | ||
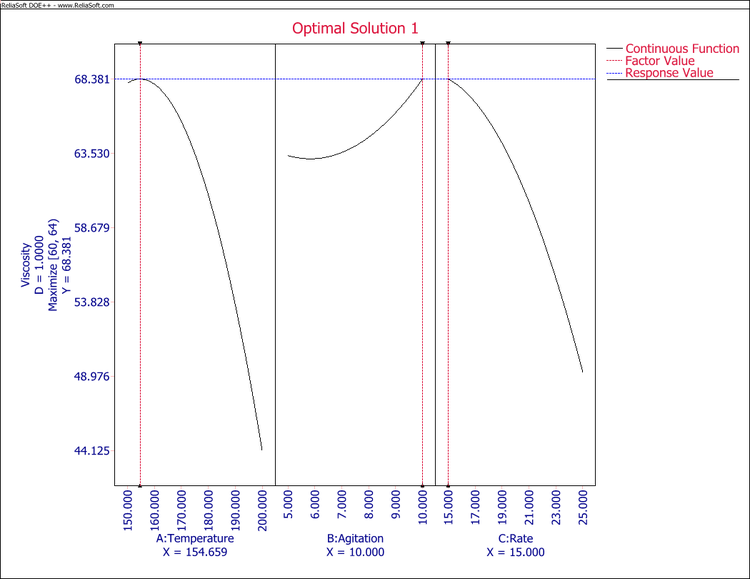
The maximum | The maximum viscosity is shown in the following optimal solution plot. | ||
[[Image:behnken_plot.png|center|750px]] | [[Image:behnken_plot.png|center|750px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:08, 18 September 2023
New format available! This reference is now available in a new format that offers faster page load, improved display for calculations and images and more targeted search.
As of January 2024, this Reliawiki page will not continue to be updated. Please update all links and bookmarks to the latest references at DOE examples and DOE reference examples.