Monte Carlo Simulation Example: Difference between revisions
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) m (moved Template:Example: Monte Carlo Simulation A Hinge Length Example to Monte Carlo Simulation Example: incorrect namespace) |
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) (updated example) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'' | <noinclude>{{Banner Weibull Examples}} | ||
''A variation of this example appears in the [http://help.synthesis8.com/weibull_alta8/user-defined_equation_example.htm|<nowiki>Weibull++/ALTA</nowiki> Help file]''. | |||
A hinge is made up of four components A, B, C, D. Seven units of each component | |||
</noinclude>'''Monte Carlo Simulation: A Hinge Length Example''' | |||
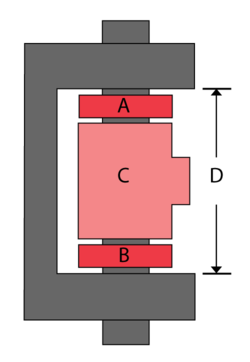
A hinge is made up of four components A, B, C, D, as shown next. Seven units of each component were taken from the assembly line and the following measurements (in cm) were recorded: | |||
| Line 14: | Line 18: | ||
\text{1}\text{.984} & \text{1}\text{.9908} & \text{30}\text{.0423} & \text{35}\text{.7111} \\ | \text{1}\text{.984} & \text{1}\text{.9908} & \text{30}\text{.0423} & \text{35}\text{.7111} \\ | ||
\end{matrix}</math> | \end{matrix}</math> | ||
[[Image:WB.23 lda26.1.png|center|250px| ]] | [[Image:WB.23 lda26.1.png|center|250px| ]] | ||
Determine the | |||
Determine the probability that the stress of the A, B and C components will result to the value of D falling out of specification. | |||
'''Solution''' | '''Solution''' | ||
In a Weibull++ standard folio, enter the parts dimensions measurements of each component into a separate data sheets. Analyze each data sheet using the normal distribution and the RRX analysis method. The parameters are: | |||
| Line 32: | Line 38: | ||
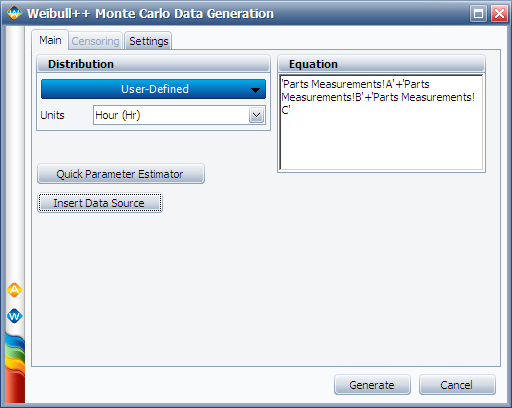
Next, perform a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate the probability that (A+B+C) will be greater than D. To do this, choose the '''User Defined''' distribution and enter its equation as follows. (Click the '''Insert Data Source''' button to insert the data sheets that contain the measurements for the components.) | |||
[[Image:Rsik Analysis Example Monte Carlo Setting.png|thumb|center|550px| ]] | |||
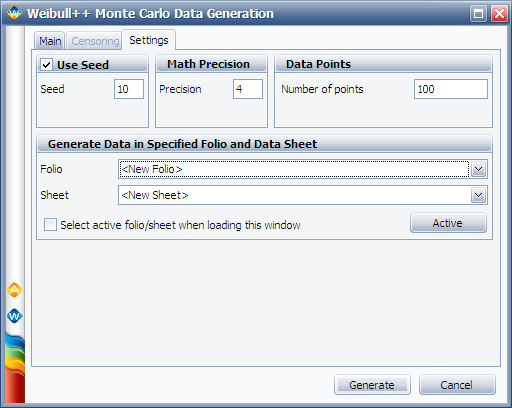
On the Setting tab, set the number of data points to '''100''', as shown next. | |||
[[Image:Rsik Analysis Example Monte Carlo Number of Points.png|thumb|center|550px| ]] | |||
Click '''Generate''' to create a data sheet that contains the generated data points. Rename the new data sheet to "Simulated (A+B+C)." | |||
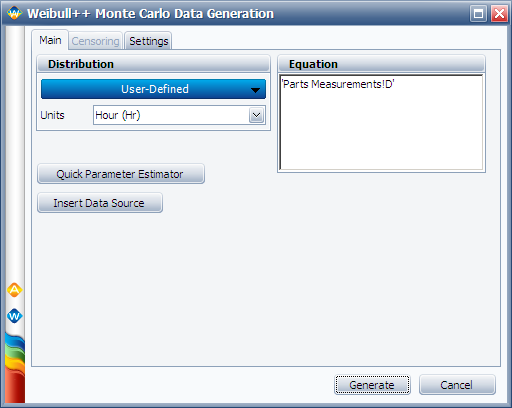
Follow the same procedure to generate 100 data points to represent the D measurements. Rename the new data sheet to "Simulated D." | |||
[[Image:Rsik Analysis Example Monte Carlo D.png|thumb|center|550px| ]] | |||
Analyze the two data sets, "Simulated (A+B+C)" and "Simulated D," using the normal distribution and the RRX analysis method. | |||
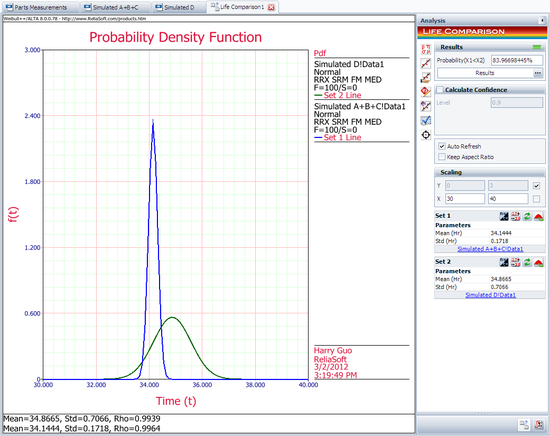
Next, open the Life Comparison tool and choose to compare the two data sheets. The following picture shows the ''pdf'' curves of the two data sets. | |||
[[Image:Rsik Analysis Example Selected Life | [[Image:Rsik Analysis Example Selected Life Comparison Plot.png|thumb|center|550px| ]] | ||
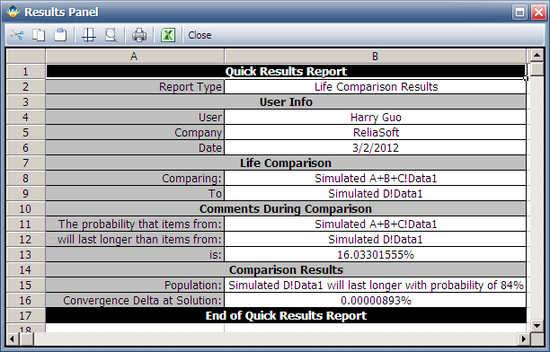
The following report shows that the probability that (A+B+C) will be greater than D is 16.033%. (Note that the results may vary because of the randomness in the simulation.) | |||
[[Image:Rsik Analysis Example Selected Life Comparison Result.png|thumb|center|550px| ]] | |||
Revision as of 06:46, 30 July 2012
New format available! This reference is now available in a new format that offers faster page load, improved display for calculations and images and more targeted search.
As of January 2024, this Reliawiki page will not continue to be updated. Please update all links and bookmarks to the latest references at Weibull examples and Weibull reference examples.
A variation of this example appears in the Weibull++/ALTA Help file.
Monte Carlo Simulation: A Hinge Length Example
A hinge is made up of four components A, B, C, D, as shown next. Seven units of each component were taken from the assembly line and the following measurements (in cm) were recorded:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{matrix} \text{Dimensions for A} & \text{Dimensions for B} & \text{Dimensions for C} & \text{Dimensions for D} \\ \text{2}\text{.0187} & \text{1}\text{.9795} & \text{30}\text{.4216} & \text{33}\text{.6573} \\ \text{1}\text{.9996} & \text{2}\text{.0288} & \text{29}\text{.9818} & \text{34}\text{.5432} \\ \text{2}\text{.0167} & \text{1}\text{.9883} & \text{29}\text{.9724} & \text{34}\text{.6218} \\ \text{2}\text{.0329} & \text{2}\text{.0327} & \text{30}\text{.192} & \text{34}\text{.7538} \\ \text{2}\text{.0233} & \text{2}\text{.0119} & \text{29}\text{.9421} & \text{35}\text{.1508} \\ \text{2}\text{.0273} & \text{2}\text{.0354} & \text{30}\text{.1343} & \text{35}\text{.2666} \\ \text{1}\text{.984} & \text{1}\text{.9908} & \text{30}\text{.0423} & \text{35}\text{.7111} \\ \end{matrix} }[/math]
Determine the probability that the stress of the A, B and C components will result to the value of D falling out of specification.
Solution
In a Weibull++ standard folio, enter the parts dimensions measurements of each component into a separate data sheets. Analyze each data sheet using the normal distribution and the RRX analysis method. The parameters are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{matrix} \text{A} & \text{B} & \text{C} & \text{D} \\ \hat{\mu }=2.0146 & \hat{\mu }=2.0096 & \hat{\mu }=30.0981 & \hat{\mu }=34.8149 \\ \hat{\sigma }=0.0181 & \hat{\sigma }=0.0249 & \hat{\sigma }=0.1762 & \hat{\sigma }=0.7121 \\ \end{matrix} }[/math]
Next, perform a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate the probability that (A+B+C) will be greater than D. To do this, choose the User Defined distribution and enter its equation as follows. (Click the Insert Data Source button to insert the data sheets that contain the measurements for the components.)
On the Setting tab, set the number of data points to 100, as shown next.
Click Generate to create a data sheet that contains the generated data points. Rename the new data sheet to "Simulated (A+B+C)."
Follow the same procedure to generate 100 data points to represent the D measurements. Rename the new data sheet to "Simulated D."
Analyze the two data sets, "Simulated (A+B+C)" and "Simulated D," using the normal distribution and the RRX analysis method.
Next, open the Life Comparison tool and choose to compare the two data sheets. The following picture shows the pdf curves of the two data sets.
The following report shows that the probability that (A+B+C) will be greater than D is 16.033%. (Note that the results may vary because of the randomness in the simulation.)