Non-Parametric RDA Transmission Example: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Recurrent | '''Non-Parametric Recurrent Event Data Analysis Transmission Example''' | ||
The following table shows the repairs on a sample of 14 cars with manual transmission in a preproduction road test [[Appendix: Weibull References|[31]]]. Here + denotes the censoring ages (how long a car has been observed). | |||
<center><math>\begin{matrix} | <center><math>\begin{matrix} | ||
Car ID & Mileage \\ | Car ID & Mileage \\ | ||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
\text{14} & \text{3240, 7690, 18965+} \\ | \text{14} & \text{3240, 7690, 18965+} \\ | ||
\end{matrix}</math></center> | \end{matrix}</math></center> | ||
The car manufacturer seeks to estimate the mean cumulative number of repairs per car by 24,000 test miles (equivalently 5.5 x 24,000 = 132,000 customer miles) and to observe whether the population repair rate increases or decreases as a population ages. | |||
<br>'''Solution''' | |||
'''Solution''' | |||
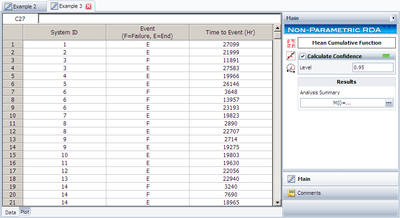
The data is entered into a | The data is entered into a non-parametric RDA folio in Weibull++ as follows. | ||
[[Image:Recurrent Data Example 3 Data.png|thumb|center|400px | [[Image:Recurrent Data Example 3 Data.png|thumb|center|400px]] | ||
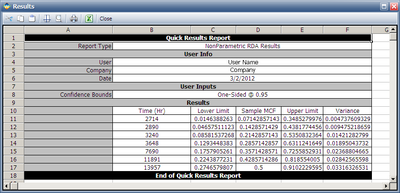
The results are as follows, | The results are as follows, | ||
[[Image:Recurrent Data Example 3 Result.png|thumb|center|400px | [[Image:Recurrent Data Example 3 Result.png|thumb|center|400px]] | ||
The results indicate that after 13,957 miles of testing, the estimated mean cumulative number of repairs per car is 0.5. Therefore, by 24,000 test miles, the estimated mean cumulative number of repairs per car is 0.5. | The results indicate that after 13,957 miles of testing, the estimated mean cumulative number of repairs per car is 0.5. Therefore, by 24,000 test miles, the estimated mean cumulative number of repairs per car is 0.5. | ||
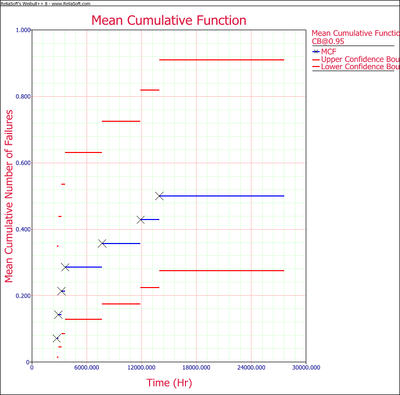
The MCF plot is shown next. | The MCF plot is shown next. | ||
[[Image:Recurrent Data Example 3 Plot.png|thumb|center|400px | [[Image:Recurrent Data Example 3 Plot.png|thumb|center|400px]] | ||
A smooth curve through the MCF plot has a derivative that decreases as the population ages. That is, the repair rate decreases as each population ages. This is typical of products with manufacturing defects. | A smooth curve through the MCF plot has a derivative that decreases as the population ages. That is, the repair rate decreases as each population ages. This is typical of products with manufacturing defects. | ||
Revision as of 16:55, 8 March 2012
Non-Parametric Recurrent Event Data Analysis Transmission Example
The following table shows the repairs on a sample of 14 cars with manual transmission in a preproduction road test [31]. Here + denotes the censoring ages (how long a car has been observed).
The car manufacturer seeks to estimate the mean cumulative number of repairs per car by 24,000 test miles (equivalently 5.5 x 24,000 = 132,000 customer miles) and to observe whether the population repair rate increases or decreases as a population ages.
Solution
The data is entered into a non-parametric RDA folio in Weibull++ as follows.
The results are as follows,
The results indicate that after 13,957 miles of testing, the estimated mean cumulative number of repairs per car is 0.5. Therefore, by 24,000 test miles, the estimated mean cumulative number of repairs per car is 0.5.
The MCF plot is shown next.
A smooth curve through the MCF plot has a derivative that decreases as the population ages. That is, the repair rate decreases as each population ages. This is typical of products with manufacturing defects.