Stress-Strength Analysis in Design for Reliability
Using Stress-Strength Analysis to Determine the Required Strength Distribution
Assume that the stress distribution for a component is known and it is a Weibull distribution with beta=3 and eta=2000. For the current design, the strength distribution is also a Weibull distribution with beta =1.5 and eta=4000.
- • Evaluate the current reliability.
- • If the reliability does not meet the target reliability of 90%, determine what parameters would be required for the strength distribution in order to meet the specified target.
Solution
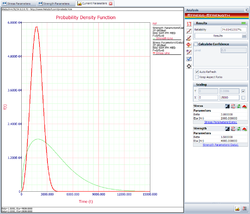
The following picture shows the stress-strength tool and the calculated reliability of the current design.
The result shows that the current reliability is about 74.05%, which is below the target value of 90%. We need to use the Target Reliability Parameter Estimator to determine the parameters for the strength distribution that would be required to meet the target.
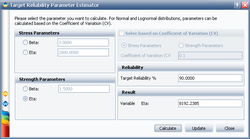
The following picture shows the Target Reliability Parameter Estimator window. In the Strength Parameters area, select eta. Set the Target Reliability to 90% and click Calculate:
The calculated eta is 8192.2385 hours. Click Update to perform the stress-strength analysis again using the altered parameters for the strength distribution.
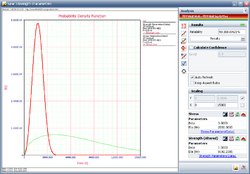
The following plot shows that the calculated reliability is 90%. Therefore, in order to meet the reliability requirement, the component must be redesigned such that the eta parameter of the strength distribution is at least 8192.2385 hours.