Template:Example: Lognormal Distribution RRY: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
{|align="center" border=1 cellspacing=0 | {|align="center" border=1 cellspacing=0 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="text-align:center"| Table - Life Test Data | |colspan="2" style="text-align:center"| Table 1 - Life Test Data | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Data point index | !Data point index | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
'''Solution''' | '''Solution''' | ||
Construct Table | Construct Table 2, as shown next. | ||
<center><math>\overset{{}}{\mathop{\text{Table | <center><math>\overset{{}}{\mathop{\text{Table }\text{2 - Least Squares Analysis}}}\,</math></center> | ||
<center><math>\begin{matrix} | <center><math>\begin{matrix} | ||
Revision as of 16:57, 2 March 2012
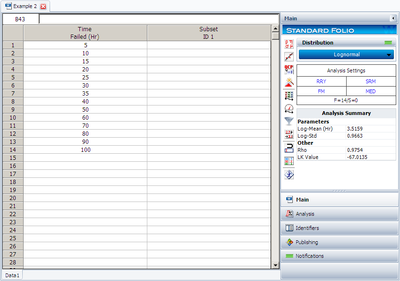
Lognormal Distribution RRY Example
Fourteen units were reliability tested and the following life test data were obtained:
| Table 1 - Life Test Data | |
| Data point index | Time-to-failure |
|---|---|
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 15 |
| 4 | 20 |
| 5 | 25 |
| 6 | 30 |
| 7 | 35 |
| 8 | 40 |
| 9 | 50 |
| 10 | 60 |
| 11 | 70 |
| 12 | 80 |
| 13 | 90 |
| 14 | 100 |
Assuming the data follow a lognormal distribution, estimate the parameters and the correlation coefficient, [math]\displaystyle{ \rho }[/math] , using rank regression on Y.
Solution
Construct Table 2, as shown next.
The median rank values ( [math]\displaystyle{ F({{t}_{i}}) }[/math] ) can be found in rank tables or by using the Quick Statistical Reference in Weibull++ .
The [math]\displaystyle{ {{y}_{i}} }[/math] values were obtained from the standardized normal distribution's area tables by entering for [math]\displaystyle{ F(z) }[/math] and getting the corresponding [math]\displaystyle{ z }[/math] value ( [math]\displaystyle{ {{y}_{i}} }[/math] ).
Given the values in the table above, calculate [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{a} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{b} }[/math]:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & \widehat{b}= & \frac{\underset{i=1}{\overset{14}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,t_{i}^{\prime }{{y}_{i}}-(\underset{i=1}{\overset{14}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,t_{i}^{\prime })(\underset{i=1}{\overset{14}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,{{y}_{i}})/14}{\underset{i=1}{\overset{14}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,t_{i}^{\prime 2}-{{(\underset{i=1}{\overset{14}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,t_{i}^{\prime })}^{2}}/14} \\ & & \\ & \widehat{b}= & \frac{10.4473-(49.2220)(0)/14}{183.1530-{{(49.2220)}^{2}}/14} \end{align} }[/math]
or:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{b}=1.0349 }[/math]
and:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{a}=\frac{\underset{i=1}{\overset{N}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,{{y}_{i}}}{N}-\widehat{b}\frac{\underset{i=1}{\overset{N}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,t_{i}^{\prime }}{N} }[/math]
or:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{a}=\frac{0}{14}-(1.0349)\frac{49.2220}{14}=-3.6386 }[/math]
- Therefore:
- [math]\displaystyle{ {\sigma'}=\frac{1}{\widehat{b}}=\frac{1}{1.0349}=0.9663 }[/math]
and:
- [math]\displaystyle{ {\mu }'=-\widehat{a}\cdot {\sigma'}=-(-3.6386)\cdot 0.9663 }[/math]
or:
- [math]\displaystyle{ {\mu }'=3.516 }[/math]
The mean and the standard deviation of the lognormal distribution are obtained using equations in section Lognormal Statistical Properties:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{T}=\mu ={{e}^{3.516+\tfrac{1}{2}{{0.9663}^{2}}}}=53.6707\text{ hours} }[/math]
and:
- [math]\displaystyle{ {\sigma}=\sqrt{({{e}^{2\cdot 3.516+{{0.9663}^{2}}}})({{e}^{{{0.9663}^{2}}}}-1)}=66.69\text{ hours} }[/math]
The correlation coefficient can be estimated as:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{\rho }=0.9754 }[/math]
The above example can be repeated using Weibull++ , using RRY.
The mean can be obtained from the QCP and both the mean and the standard deviation can be obtained from the Function Wizard.